Schizophrenia – Risk factors and warning signs
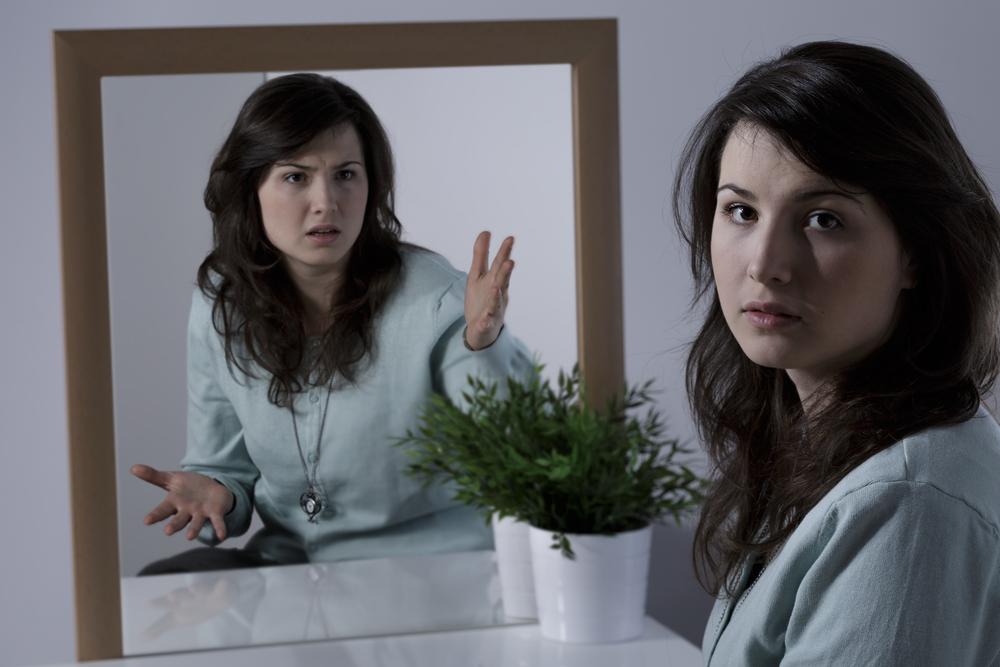
A long-term mental disorder that involves emotional and behavioral breakdown is termed as schizophrenia. People diagnosed with this disorder exhibit faulty behavior, withdrawal symptoms, and inappropriate actions. It is a chronic brain disorder that affects around 1.2% of the population in the country itself.
The main challenge in understanding schizophrenia is its complexity and the misconceptions that surround it. Some people mistake it for split or multiple personality disorder. Mostly, those affected by this disorder are not violent or harmful. As per research, this mental disorder affects men and women equally, but it may exhibit an earlier onset in men.
Risk factors of schizophrenia
There are a number of genetic and environmental factors that contribute to schizophrenia.
Family history : People who have a first-degree relative affected by the disease are known to be at a higher risk of developing schizophrenia. When one of the parents is affected by this disorder, the children have a 13% risk of developing the same. If both parents affected by this disorder, the children have a 36% chance of being affected.
Other risk factors : Based on various studies, certain risk factors related to schizophrenia among different groups were found.
- Living in a densely populated area.
- Prenatal exposure to hunger; children born to women who have been through famine during the first three months of pregnancy have a higher risk of developing the disorder.
- Although stress and schizophrenia are not directly liked, some researchers believe prolonged stress may cause the disease.
Warning signs of schizophrenia
People affected with schizophrenia may not have clarity between real and unreal experiences. The severity and duration of the symptoms will vary from one person to another. A typical characteristic of this disorder is that the incidence of severe psychotic episodes decreases during the affected person’s lifetime. Those who do not take their medications regularly or indulge in drugs and alcohol while undergoing treatment may experience an increase in the symptoms.
Positive psychotic symptoms : Symptoms such as hallucinations, paranoid delusions, distorted perceptions, unpredictable behavior, and exaggerated behavior may be classified as positive psychotic symptoms.
Negative psychotic symptoms : A marked decline in a person’s ability to initiate or organize plans, speak or express feelings, or find joy may be categorized as negative psychotic symptoms.
Disorganization symptoms : Confusion or distorted thinking and speech, inability to think logically, and abnormal behavior may be categorized as disorganization symptoms.
Impaired cognition : Issues with concentration, memory, attention, and job/school performance are associated with impaired cognition symptoms.
While there is no cure for schizophrenia, more research findings are leading to new and effective treatment options. Researchers are looking at the causes of the disease through genetics, behavioral research, and advanced brain imaging techniques. Newer research findings enable more effective treatment for the disorder.