Sleep apnea – Risk factors, effects, and symptoms
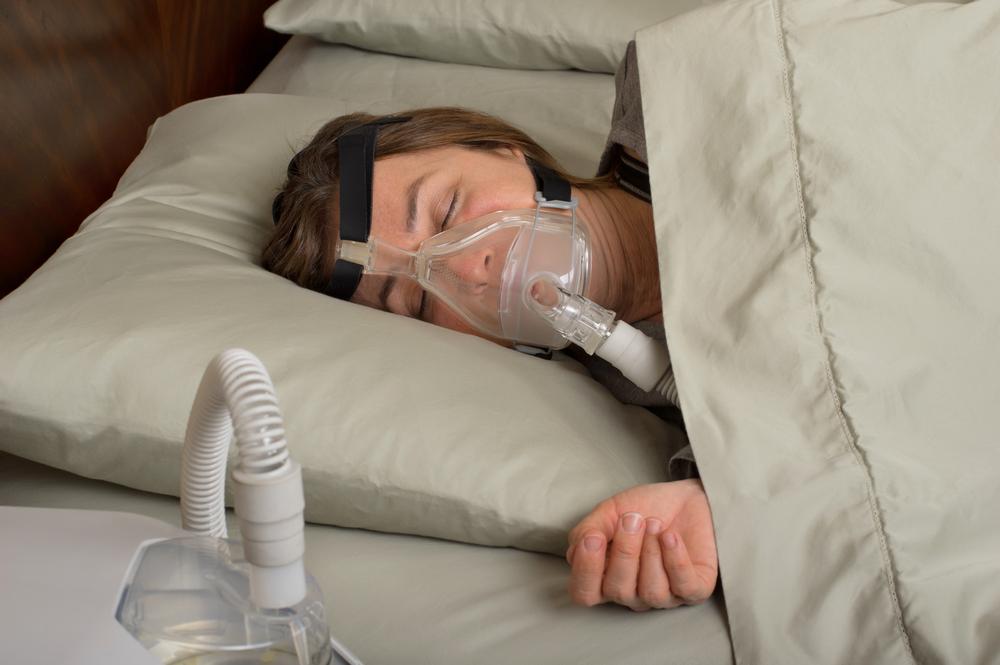
Sleep apnea is a disorder where the patient experience interrupted breathing while sleeping. Patients might stop breathing in their sleep numerous times. This situation can happen when the brain and other parts of the body do not get their required amount of oxygen. Sleep apnea can be of two types — Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) and Central Sleep Apnea (CSA). The first type is caused when the soft tissues at the back of the throat collapse during sleep, causing a blockage in the airway. The second type is caused when the brain is unable to send signals to the muscle to breathe.
Risk factors and effects of sleep apnea
Some factors can increase an individual’s risk of developing sleep apnea. Here are the risk factors:
- Being overweight: People who have a body mass index (BMI) of 25 or more are prone to developing sleep apnea
- Having a larger neck size: People with a larger neck size are likely to develop sleep apnea because they have more soft tissue which can block the air passage during sleep.
- Heredity: A person is more likely to develop sleep apnea if they have an immediate family member who suffers from the same disease.
- Middle-aged men: Scientists haven’t uncovered why middle-aged men are more likely to develop sleep apnea as compared to people of other genders and age groups. Women are more likely to develop sleep apnea when they are reaching their menopausal stage.
Sleep apnea, if left untreated, can lead to other health problems. Some of these are:
- High blood pressure, which is quite common in patients with sleep apnea
- Sleep apnea may lead to brain stroke in some people
- It can also lead to irregular heartbeats, resulting in heart attacks or heart failure
- Patients are likely to develop depression
- Sleep apnea can lead to a headache in some patients
- Furthermore, sleep apnea can make patients feel sleepy during the day. It may lead to underperformance at the workplace or school. Patients are also more likely to get into road accidents while driving due to the problems associated with this condition.
When to consult a physician for sleep apnea
Sleep apnea has some common symptoms which help to raise the alarm for patients so that they can consult a physician for the diagnosis and treatment. Various physical exams help in the diagnosis of sleep apnea. However, one should look out for the following symptoms to identify this condition:
- Snoring: One of the common symptoms for sleep apnea is loud or frequent snoring followed by pauses in breathing or gasping sound.
- Fatigue: Patients might experience fatigue or sleepiness during the daytime.
- Difficulty in sleep: Patients with this disorder might experience difficulty in sleeping, followed by headaches in the morning. They may also wake up frequently at night to use the bathroom.
- Loss of memory: Patients might experience a loss of memory.
- Lack of concentration: Patients might experience difficulties in concentrating.
If detected on time, patients can be treated with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) mask that helps in keeping the upper airway passage open by providing enough air pressure. It can help in preventing sleep apnea.