Treatment and prevention of melanoma
Diagnosing melanoma involves a skin examination after understanding the medical history of the patient. All melanoma risk factors are considered to enable accurate diagnosis, given the fact that some types of melanoma are difficult to diagnose.
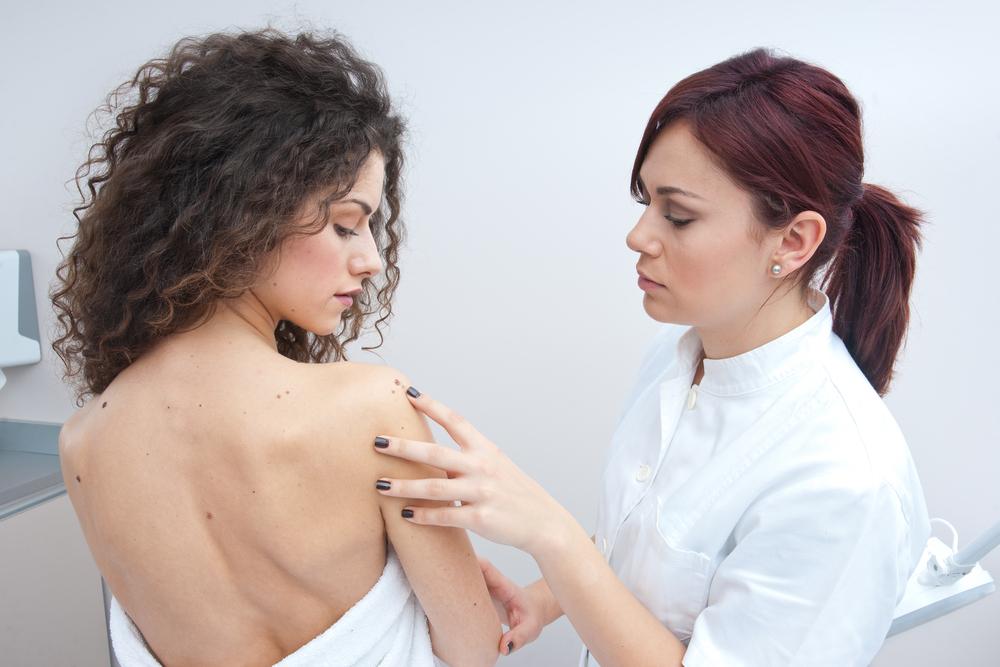
A skin examination by a physician may identify the visible lumps, nodules or abnormal areas on the skin. The doctor will note the size, shape, color, and texture of and changes to the suspected areas. Symptoms peculiar to the mucosal melanoma will prompt the doctor to look at susceptible sites for lesions, discolored patches, and lesions. The lymph nodes will be examined for enlargement, which is a sure sign of spreading cancer. Dermatologists may use dermatoscopy, which involves the examination of the skin using a dermatoscope.
After identifying such areas, the normal course is to take samples for biopsies. There are typically four types of biopsies used: shave, punch, incisional, and excisional. A shave biopsy takes a small layer from the top of the skin. A punch biopsy uses a tool to make a hole in the melanoma and take out a portion as a sample. An incisional biopsy cuts out a portion of the melanoma while an excisional biopsy cuts out the entire melanoma along with a margin of healthy tissue to ensure that the entire melanoma has been removed.
If the melanoma is suspected to have spread to the lymph nodes other types of biopsies are conducted. A fine-needle aspiration biopsy is used on enlarged lymph nodes. The excisional lymph node biopsy is used to remove the entire lymph node that may be affected by the melanoma. A sentinel lymph node biopsy is used to check if the melanoma has spread to the sentinel lymph nodes around the suspected area of the melanoma.
The biopsies are tested in a pathology lab for the presence of melanoma and to see if there are gene mutations, so that appropriate treatment options are selected.
Further, imaging tests including CT scans, MRI scans, PET scans, and chest x-rays are used to check the extent of the metastasis, and the efficacy of the treatment.
Staging melanoma is to determine the prognosis, best course of treatment and probable outcomes. The TNM system broadly classifies a melanoma into T for near, N for regional and M for distant, based on the spread of the disease. Within each of these broad classifications are multiple stages that describe different conditions of the melanoma.
The various treatment options include
- Surgery
Excisional skin biopsies remove the entire melanoma but further surgery is required to reduce the chances of recurrence. If the melanoma has spread to the nearby (sentinel) lymph nodes, they too will be removed. - Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is administered through oral medications and intravenous injection. The medications destroy the melanoma cells. A specialized method called isolated limb perfusion is used to localize the effect of the medications by blocking the flow of blood from the limb to the rest of the body. - Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy uses specific medications to target the vulnerabilities in the melanoma cells. Targeted therapy is used only in certain cases of melanoma. It has a number of side effects including fever, chills, dehydration and skin problems. - Immunotherapy
This treatment uses medications to boost the function of the immune system to help fight the melanoma. The substances used may be produced by the body or are synthesized in a laboratory. Side effects of this treatment include fatigue, fever, chills, headache, and muscle ache. - Radiation
Radiation is used in most local and regional melanomas or patients whose melanomas cannot be surgically removed. Radiation has been known to reduce local recurrence but has no effect on the survival of the patient.
There a few precautions that can be taken to reduce the risk of melanoma.
- Be aware of the condition of the skin and watch of any changes.
- Wear protective clothing including socks and shoes to avoid exposure to the sun, avoid going out in the sun during the middle of the day and avoid sunburn.
- Wear sunscreen cream or lotion always.
- Avoid tanning beds and sun lamps.
- If there is any suspected patch, growth or lump get medical help to enable early detection.